Arthritis affects 350 million people worldwide, including both adults and children. Arthritis attacks a person’s joints and causes both inflammation and pain. Nevertheless, what creates arthritis and how do you know if that is the pain you are experiencing? We will cover that information here, along with treatment options.
Arthritis in Children
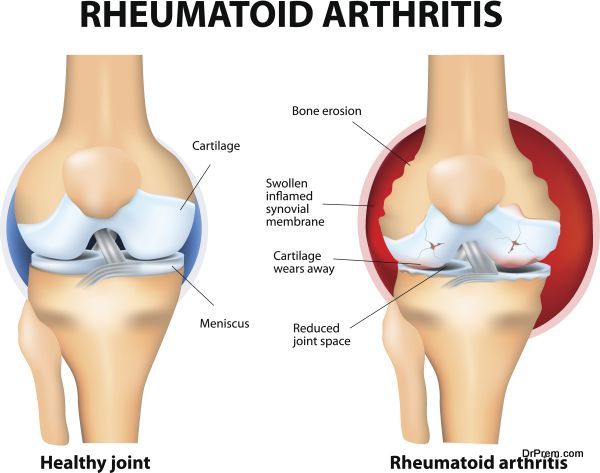
Because arthritis can affect both children and adults, symptoms can vary in severity and sometimes are misdiagnosed. Arthritis pain in young children is known as juvenile arthritis and is marked by pain in the joints due to swelling of the synovium, or the tissue that lines your joints.
Unfortunately, the cause of juvenile arthritis is unknown, though some potential triggers may be from the child’s environment, genetics, or infections.
Arthritis is also considered an autoimmune disease, which is when the immune system attacks the body instead of protecting it. There are actually five different types of juvenile arthritis, each having its own set of symptoms. Here is a quick overview.
- Polyarthritis: This type of juvenile arthritis closely resembles arthritis in adults and generally attacks the same joints on both sides of the body, in five different areas. It can attack the neck and jaw, as well as the hands and feet. It’s also seen more often in girls than boys.
- Systemic: Also known as Still’s disease, this type of arthritis can involve many systems of the body and affect many different areas. A rash often accompanies joint pain on the arms and legs, and a high fever. Organs are also at risk of systemic arthritis including the liver, heart, and lymph nodes.
- Oligoarthritis: This is rheumatoid arthritis in youths. It affects less than five joints, most commonly the ankles, knees or wrists. This type of arthritis can also attack the iris of a child’s eye. Symptoms usually subside once a juvenile enters adulthood.
- Enthesitis-related Arthritis: This arthritis affects the spine, eyes, hips and areas where a child’s tendons attach to the bones. Enthesitis-related arthritis typically affects boys age 8 or older and is often genetically linked.
- Psoriatic: Children with this type of arthritis also have a skin disorder known as psoriasis. The two disorders go hand in hand and either can manifest first.
Symptoms of Arthritis in kids
Symptoms of each type of arthritis can be different but the general symptoms include:
- Joint pain and swelling
- Blurry vision
- Rash
- Fever
- Weight loss
- Limping
- Irritability
Symptoms can manifest themselves differently in children of varying ages, so it is important to consult with a medical professional.
Treatment for Arthritis in Kids

Treatment options for juvenile arthritis depend on the type, which must be diagnosed first. This can be difficult since there is not one test that determines juvenile arthritis. Some methods for diagnosis include blood tests, bone scans, x-rays and other imaging tests. Some of these tests are done to rule out other diseases or infections with similar symptoms such as Lyme disease.
Once the type of arthritis is determined, treatment can begin. The most common forms of treatment include some medications for reduced swelling and pain management, as well as exercises. The goal of treatment in kids is to help reduce the current discomfort, but also prevent prolonged joint damage and improve current mobility and strength.
Arthritis in Adults
Like juvenile arthritis, there are several different types of arthritis in adults, and unfortunately, arthritis only worsens with age. The most common types are rheumatoid, osteoporosis, psoriatic, fibromyalgia and gout. Let’s look at these types a little closer.
- Gout: Most commonly found in the feet, severe pain generally begins in the big toe but can affect the ankles and knees as well. Gout is caused by a high level of uric acid in the blood.
- Fibromyalgia: Symptoms of fibromyalgia aren’t specific to pain. Sufferers can experience sleep disturbance, anxiety and mood changes. These symptoms are accompanied by widespread chronic pain.
- Osteoporosis: A common form of arthritis, osteoporosis is caused by the breakdown of tissue in the bone, resulting in thinning bones with low density. Individuals with osteoporosis are more susceptible to fractures.
- Rheumatoid: The same as in a juvenile, rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease and is marked by symptoms like high fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, and joint pain.
- Psoriatic: Again, this type of arthritis manifests itself similarly in both youth and adults and is accompanied by psoriasis.
Diagnosis and Treatment
The diagnosis of arthritis in adults is similar to that of children. Several blood and imaging tests are performed to help determine the cause and type of arthritis in patients. Doctors will also discuss symptoms, length of time, and any other underlying health conditions to help properly diagnose arthritis in adults. Treatment options vary and may differ slightly than those in children.
Medication

There are a long list of arthritis medications available. Prescription is often based on symptoms, as well as any other medications a patient is currently taking. A common type of medication for treating arthritis is non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, also known as NSAIDs. These types of drugs help to reduce both swelling and pain.
NSAIDs are available in both oral and cream form. Arthritis creams are rubbed directly on the joints and affected areas. Other medications, such as analgesics help reduce inflammation but don’t offer pain relief for arthritis sufferers. Specific types of arthritis may require specific medications.
Therapy
Because arthritis affects the joints and muscles in a person’s body, physical therapy can sometimes offer relief for pain and discomfort. Physical therapy increases mobility and increase a person’s range of motion. Therapy may also help strengthen muscles surrounding the affected joint. Some therapists may also recommend a splint or brace for future support.
Surgery
If the above-mentioned methods of treatment don’t offer relief, some patients may be candidates for surgery. There are several surgical options available, depending on the affected area and severity of the condition. These options include join repair, fusion and replacement.
- Repair: This is the least invasive of surgeries and involves the joint surfaces being smoothed or realigned. This helps to reduce pain and improve mobility and function.
- Fusion: Common in small joints like those found in ankles, wrists or fingers, surgeons remove the ends of the two bones and then fuses them together. This allows them to heal into one unit.
- Replacement: The most extreme option, joint replacement is exactly what it sounds like. A patient’s joint is removed and replaced with an artificial one. This is most commonly performed for hips and knees.
Options are Available
Because arthritis is such a common condition affecting both the young and old, there are numerous treatment options from therapy and medication to surgery, if needed. Pain management and reduced inflammation are also the focus of many doctors treating arthritis patients. Be sure to speak to a medical professional to discuss your symptoms and help determine which form of arthritis you have. This will guide you in choosing the right treatment plan.
Article Submitted By Community Writer




