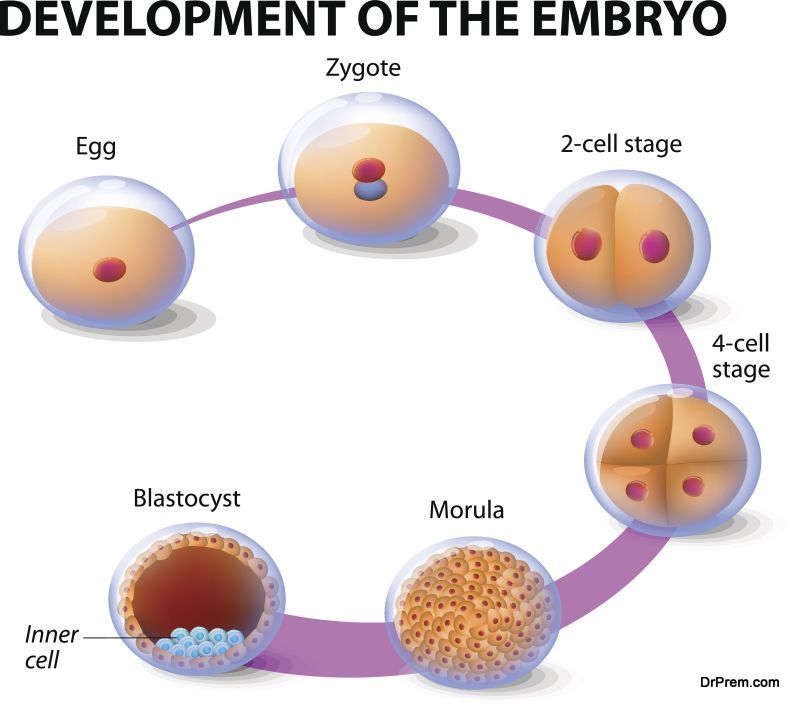
Long after the birth of a child, mothers often get the feeling that their children are within them still. This could never be proved scientifically earlier, and these feelings were supposed to be just sentimental longings. Now, scientists are saying that during pregnancy, some of the cells from the fetus can enter the body of the mother by crossing the placenta.
The gene cells then become part of the mother’s tissue. Scientists are now looking at the possibility of these cells influencing the mother’s health for better or worse, even after many decades of giving birth. Fetal cells regulate the mother’s physiology to protect from various diseases or may also increase the risk of disease. This is why pregnancy has a great effect on the body of the mother.
The effects of pregnancy on the mother’s body
The fetal-maternal conflict and its implications
The fetal maternal conflict originated millions of years ago with the first mammals which had placenta. Fetal cells manipulate mother’s body to increase nutrition from the mother. The body of the mother also has some counter measures to prevent the flow of excessive nutrition.
Once the embryo is implanted in the womb, it gets complete access to the mother’s tissues. The fetus also releases hormones to the mother, but the mother can only regulate hormones within her womb but not inside the fetus. If this hormone war remains in balance, the mother does not face any pregnancy related danger.
With the progress of the pregnancy, the fetus increases the hormone signals to increase nutrition which leads to increasing the blood pressure and blood sugar of the mother. The fetus increases the production of a hormone which releases cortisol, which stops the mother’s body from attacking the baby.
But sometimes, fetal cells regulate the mother’s physiology during pregnancy in a way which is harmful for the baby as well as the mother, leading to gestational diabetes, high blood pressure, Angelman Syndrome, Prader-Willi Syndrome. Some severe psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia, autism and bipolar disorder, childhood obesity and many cancers have been linked to the battles of hormones between mother and child.
The phenomenon of michrochimerism
The invasion of the fetal cells manipulates mother’s body and the mother carries genetic material from their babies. This is now being termed as microchimera which was named after the ‘Chimera’, the legendary beast which was made of more than one animal. Inside the mother’s body, if she has given birth to more than one baby, there would be cell remnants of all the babies. This phenomenon has been seen in humans and other mammals and scientists are trying to find out how this phenomenon evolved and the role it has in a mother’s health, including better healing of wounds and the increasing risk of cancer.
How fetal cells in the mother’s body affect her health
 Fetal cells have been found to be pluripotent, meaning that they grow/transform into different tissue types. Fetal cells circulate in the mother’s body and settle themselves in tissue. Then using the chemical clues from the surrounding cells, they grow or transform into the surrounding type of tissue. The immune system of the mother removes the unchanged cells but the fetal cells which have morphed into tissue stays undetected in the body of the mother.
Fetal cells have been found to be pluripotent, meaning that they grow/transform into different tissue types. Fetal cells circulate in the mother’s body and settle themselves in tissue. Then using the chemical clues from the surrounding cells, they grow or transform into the surrounding type of tissue. The immune system of the mother removes the unchanged cells but the fetal cells which have morphed into tissue stays undetected in the body of the mother.
Microchimerism gets complex when the mother has more than one pregnancy, as she accumulates fetal cells from each baby. Scientists are researching whether older siblings can have a hand in delaying younger sibling’s birth. Deep sequencing has allowed researchers to study microchimerism and how fetal cells regulate the mother’s physiology. Lactation could be due to residual fetal cells signaling the mother’s body to lactate.
Role of microchimerism in the mother’s health
 Scientists have found that fetal cells protect the mother from diseases like autoimmune disorders like rheumatoid arthritis. As for cancer, the evidence points both ways as mothers with breast cancer have less number of fetal cells, thus lowering the risk for breast cancer, but this is the opposite in cervical cancer.
Scientists have found that fetal cells protect the mother from diseases like autoimmune disorders like rheumatoid arthritis. As for cancer, the evidence points both ways as mothers with breast cancer have less number of fetal cells, thus lowering the risk for breast cancer, but this is the opposite in cervical cancer.
Fetal cells protect the mother from diseases of the heart by repairing the heart muscle, and healing liver and thyroid damage.
All these new information has revealed that there is more than meets the eye when it comes to pregnancy and only intensive research can ultimately determine the complex process of pregnancy and its related phenomena such as microchimerism.