Your skin is your body’s largest organ and its main job is to protect you from outside bacteria, disease, and injury. One of the most common injuries incurred by your skin are burns. When you burn your skin, it causes severe damage to the surface, killing skin cells. There are different degrees of burns categorized by the severity. This article will outline the types of burns you can suffer and how they are treated.
Types of Burns
Some burns can easily be treated at home with no lasting effects, while others require immediate medical attention and can leave permanent scarring. Here’s a breakdown of the different types of burns and how they can occur.
First Degree Burns
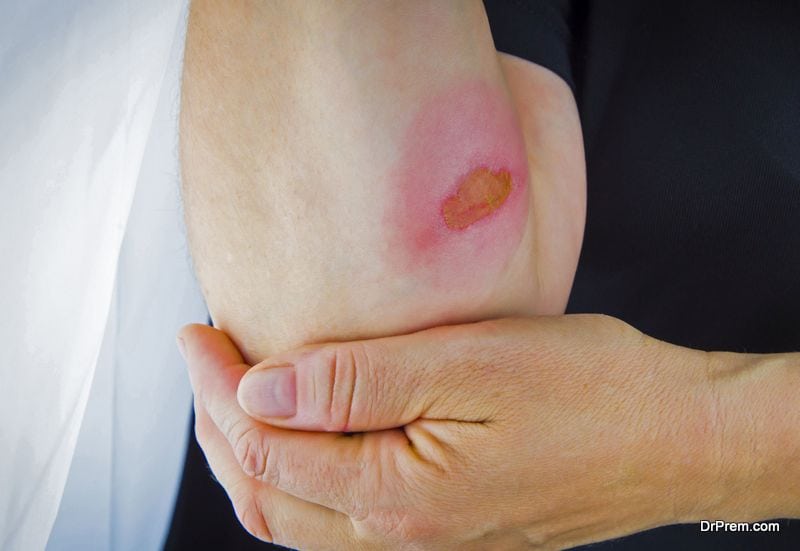
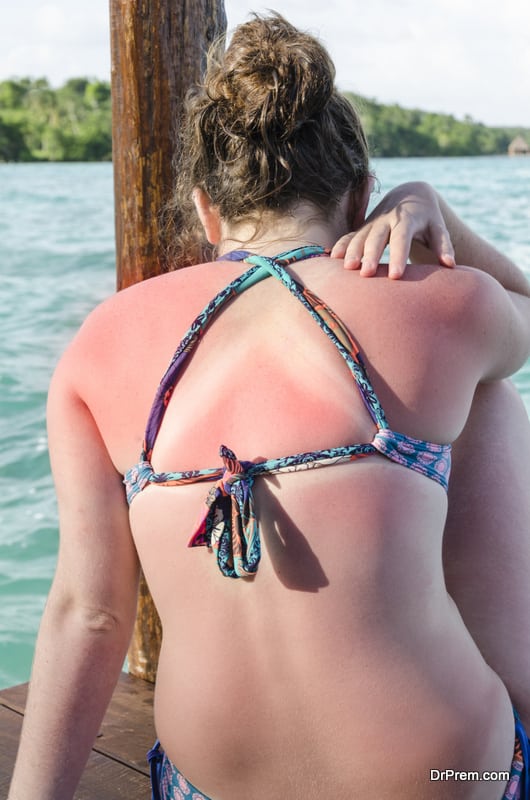 First degree burns are the most minor and only affect the upper-most layer of a person’s skin. The result of these burns is often redness and slight tenderness to the affected area. You may experience pain and swelling as well, but first degree burns don’t often blister. The most common first degree burns are caused by the following things:
First degree burns are the most minor and only affect the upper-most layer of a person’s skin. The result of these burns is often redness and slight tenderness to the affected area. You may experience pain and swelling as well, but first degree burns don’t often blister. The most common first degree burns are caused by the following things:
- Sunburn
- Scalding (from hot liquid)
- Electricity
It’s important to note that electrical burns may cause greater damage to the epidermis or run deeper, below the top layer. If you suffer an electrical burn, it’s best to seek medical attention to determine the severity of the burn.
Second Degree Burns
Second degree burns are when the burn affects more than just the top layer of skin, causing blisters and severe redness and pain. Some burns may appear wet once blisters break and release the fluid that’s held inside. As second degree burns begin to heal, scab-like tissue known as fibrinous exudate may develop where the wound once was. Second degree burns are less common than superficial, or first degree, burns, and can result from the following things:
- Sunburn
- Scalding
- Electricity
- Fire
- Chemicals
- Contact with a hot object
Although you can treat second degree burns at home when they initially occur, medical attention is often required.
Third Degree Burns
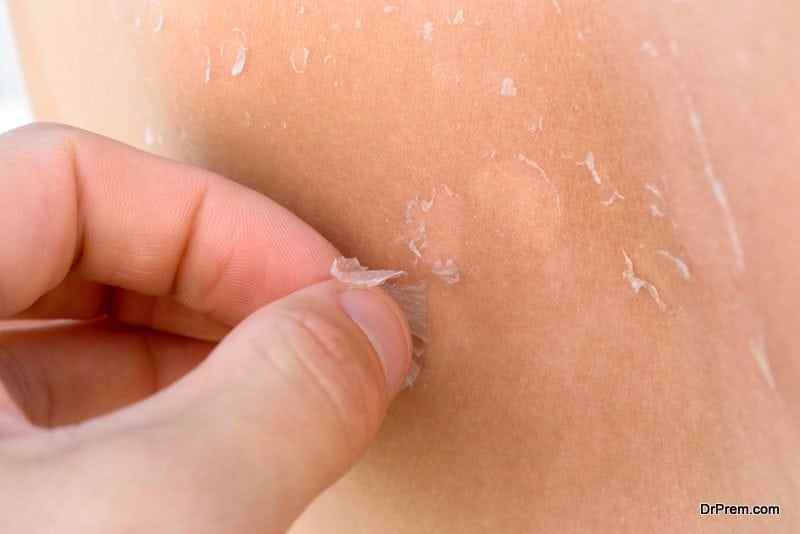 Third degree burns are the most severe type of burn and affect every layer of your outer skin. What’s surprising about third degree burns is that although they’re the most severe, they are not the most painful. This is because third degree burns cause so much damage that they may actually destroy nerve endings, which are your body’s triggers for pain. Third degree burns can appear different based on severity and the cause of the burn. Common symptoms include:
Third degree burns are the most severe type of burn and affect every layer of your outer skin. What’s surprising about third degree burns is that although they’re the most severe, they are not the most painful. This is because third degree burns cause so much damage that they may actually destroy nerve endings, which are your body’s triggers for pain. Third degree burns can appear different based on severity and the cause of the burn. Common symptoms include:
- Charred skin
- Blisters
- Raised, leathery texture
- Dark brown or white color
- Waxy appearance
Third degree burns require immediate medical attention and often result in permanent scarring. These types of burns are often caused by:
- Fire
- Electrical
- Chemical
- Scalding
- Contact with a hot object for an extended period of time
The cause of third degree burns isn’t very different from less severe burns, but instead it’s the duration and intensity of exposure to the abovementioned things that causes third degree burns to be so damaging.
Treatment Options
Different types of burns require different forms of treatment. Many first degree burns can easily be treated at home without a visit to the doctor, whereas third degree burns must be treated immediately by a medical professional. Recovery time also fluctuates depending on the severity of the burn.
First Degree Burns
 The sooner you act when treating first degree burns, the less severe the pain will be and the burn will heal faster. Some common at home techniques for treating first degree burns include:
The sooner you act when treating first degree burns, the less severe the pain will be and the burn will heal faster. Some common at home techniques for treating first degree burns include:
- Soaking the wound in cold water
- Using an anesthetic with aloe vera
- Using pain relief medications
- Covering the wound with antibiotic ointment and loose gauze
- Apply berberine to the affected area
Avoid applying ice to the affected area which may actually make matters worse. Healing for first degree burns takes between 7 and 10 days.
Second Degree Burns
Because second degree burns affect more than just the top layer of skin, treatment looks a little different. It’s important to keep these burns clean and properly bandaged to reduce the risk of infection. Other treatment options include:
- Running the burn under cold water
- Applying antibiotic cream
- Taking medications for pain relief
- Skin grafting (in severe cases)
Seek medical attention immediately if the burn covers a large area of the body or occurs to the face, hands, feet, groin, or buttocks.
Third Degree Burns
 Third degree burns cannot be treated at home and require immediate medical attention. Without proper treatment or surgery, third degree burns can cause severe scarring and further complications. These are the steps you should take following a third degree burn.
Third degree burns cannot be treated at home and require immediate medical attention. Without proper treatment or surgery, third degree burns can cause severe scarring and further complications. These are the steps you should take following a third degree burn.
- Call 911
- Raise the injury above your heart (if possible)
- Make sure no clothing is stuck to the burn
- Remain calm
Third degree burn treatment often requires skin grafting or the use of synthetic skin to treat affected areas.
Remaining calm and taking the proper avenues for burn treatment will ensure that your wounds heal properly and quickly. Avoid hot objects, scalding liquids, and always apply sunscreen when venturing outdoors. All of these measures can help prevent burns and keep you safe.
Article Submitted By Community Writer