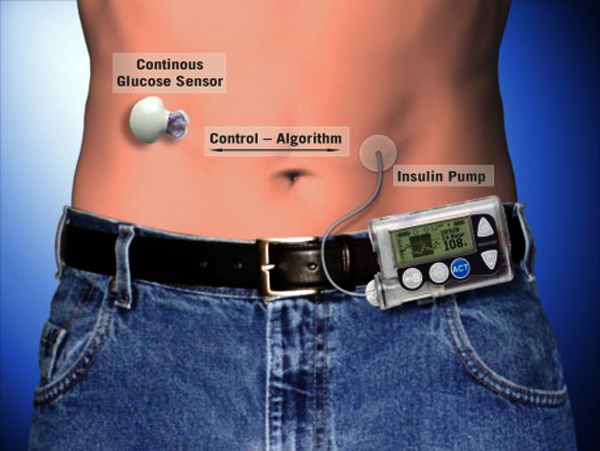
Insulin pump is one of the developments to help battle and keep diabetes under check. This is a device that digests the sugar in the blood by delivering the enzyme insulin directly into the body. It replaces the traditional medications and injections which were used as ways to get insulin into the bloodstream. It is the size of a mobile phone and can be strapped to your waist or kept in your pocket. Since it is quite convenient to carry, many diabetics are now opting for the pump. Added to this is the fact that many provincial health plans also have coverage for insulin pumps.
Working
The insulin pumps are connected to you via a thin catheter tube that goes below your skin. The pump can be programmed to work on a schedule and this is done based on three factors. The first is the basal rate. This is the minimum amount of insulin needed to maintain correct sugar levels in the blood. This gets delivered on a regular, 24-hour basis once it is programmed in.
The second factor determines the bolus dosage. This depends on the food that is partaken. Every time somebody eats, there is carbohydrate added to the system. To cover for this carbohydrate intake, insulin must be injected into the system. If not done, it may result in high blood sugar. This also can be programmed into the pump based on the size and frequency of the meals and snacks.
The third factor covers all the corrective and supplemental doses of insulin. This is in the case where the patient has high sugar even before a meal or in some other emergencies when the blood-glucose levels go high.
The pump can be neatly put away in a pocket, on the belt, in the underwear or bra, on a waistband or an armband. The tubing too can be similarly concealed. You can disconnect the pump briefly when you have a wash or bath though the pump is waterproof to a great extent. You can have it on when you sleep or go about all your activities like games and travel.
Uses
The pump is a very convenient and easy-to-use device. Since it is digitally controlled and programmable, it can deliver the doses of insulin most accurately and precisely. Even in case of an extra intake of food or any other emergency, the necessary insulin can be easily delivered. This kind of rapidity in action is possible only with an insulin pump. The patient is able to gain better control over the blood-sugar levels and ensure that there are fewer and less intense fluctuations between the highs and lows. It assures greater flexibility and freedom in terms of going out for treats or sleeping out at other’s places. Finally it saves time and energy in carefully planning each dose of insulin to be injected.
Ideal for
The insulin pump is best suited for those that require regular and large doses of insulin. Taking multiple injections could be a painful process. So instead of poking yourself four or five times daily, one could consider using the pump. Growing children, adults and even those in advanced ages are good candidates for the pump. In the beginning, the planning and regular testing that goes into programming the pump may seem tedious. But within a few days, that is over. The pump then saves the tedium of a regular insulin-injection routine. Once a person gets used to working with the pump, it almost becomes another limb of the body.
Lowdowns
The pump has its own set of disadvantages. The initial training and effort needed to get used to the working of the pump can get frustrating for some. The site of injection may have to be changed regularly else an irritation may set in. In some cases, it has been known to cause a weight gain in people. In case the catheter slips out, the patient may suffer from diabetic ketoacidosis. The most important and significant disadvantage can be the cost. The initial investment may go up as high as $7000 and require monthly supplies that cost about $200. This is where having a good insurance plan can help.