A lot of the time, skin conditions can be your body’s way of signaling other problems with your health, wellbeing, and general lifestyle.
For example, those suffering from vitiligo often find that the root cause is stress, those with eczema figure that getting more sleep lessens symptoms, and those finding a bronzing of the skin later discover they have liver failure.
And then there’s the one we’re here to discuss: those with a constant skin rash may have celiac disease.
The skin condition dermatitis herpetiformis is heavily associated with the digestive condition, which affects 1 in every 100 people around the world.
Here’s everything you need to know about the conditions, and what steps you need to take to get back on the path of health.
What is dermatitis herpetiformis?
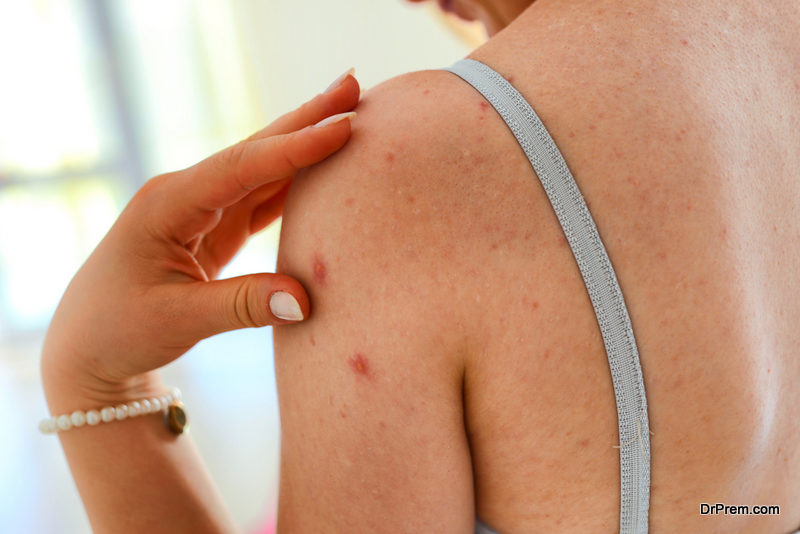 Dermatitis herpetiformis or DH is commonly referred to as a celiac or gluten rash. It is considered to be celiac disease on the skin.
Dermatitis herpetiformis or DH is commonly referred to as a celiac or gluten rash. It is considered to be celiac disease on the skin.
People suffering from the skin condition often have severely itchy and irritable skin that may blister on their elbows, knees, and buttocks.
It tends to come and go from time to time, leaving brown or pale markings behind.
If affects around 15-25% of those who have been diagnosed with celiac, and often more men than women in adulthood.
It commonly affects more people of European descent than those of African or Asian heritage.
These statistics do work the other way around, too, in that just 20% of those with the skin condition have been diagnosed with internal celiac disease, however, 80% show small signs of damage to the small intestine.
What is celiac disease?
Celiac experts imaware™ describe the disease as a ‘serious autoimmune disorder’. Those with celiac disease become unwell after eating food containing gluten, which is the protein in a range of foods acting as a type of glue to hold it together.
It is found in wheat, barley, and rye, meaning those with celiac disease will struggle to consume bread, pasta, beer, soup, baked goods, and cereals without experiencing stomach problems.
That’s because the immune system attacks its own small intestine when it finds gluten there. Without treatment, celiac disease can cause severe damage to the wall of the small intestine which makes it difficult for the body to absorb the nutrients it needs.
What are the symptoms of celiac disease?
 According to Healthcare Weekly, the symptoms of celiac disease can vary heavily from person to person.
According to Healthcare Weekly, the symptoms of celiac disease can vary heavily from person to person.
Experts claim there may be as many as 300 different symptoms of the condition, although no one experiences anywhere near all of them at one time.
Most people tend to suffer from severe fatigue, diarrhea, weight loss caused by malnutrition, stomach gas and cramping, amenia, low bone density, and even infertility.
How are the two connected?
When a person with celiac disease eats gluten, the mucosal immune system in the small intestine produces an antibody called immunoglobulin A, which is directed against the gluten proteins.
How is dermatitis herpetiformis diagnosed?
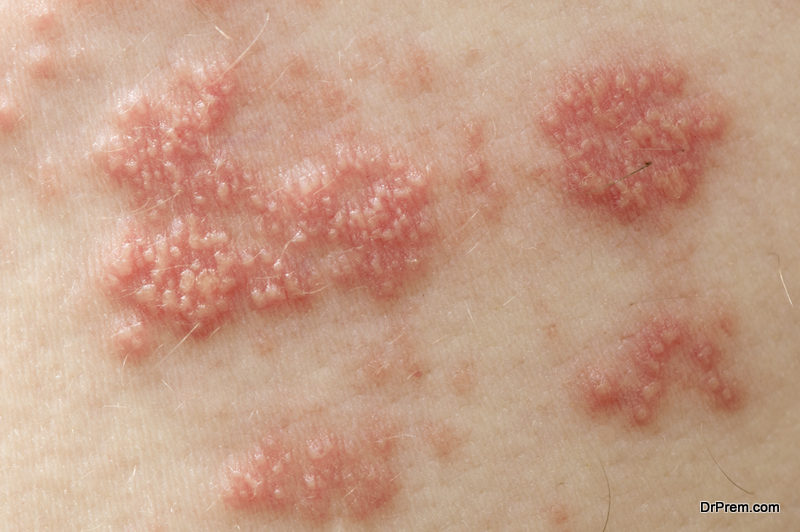 Usually, dermatologists will use a punch biopsy to confirm symptoms of DH. An area of skin with a diameter of no more than 4mm is removed and a dye is used to locate the presence of Immunoglobulin A
Usually, dermatologists will use a punch biopsy to confirm symptoms of DH. An area of skin with a diameter of no more than 4mm is removed and a dye is used to locate the presence of Immunoglobulin A
It’s important to visit a doctor who has diagnosed the condition before, claims the Celiac Disease Foundation, so they are aware of exactly how to perform the biopsy.
For example, the patch of skin should be directly adjacent to the suspected DH lesion, rather than on the lesion itself. Inflammation of the lesion can destroy IgA deposits.
How is celiac disease diagnosed
Generally, those diagnosed with DH do not need an intestinal biopsy to confirm celiac disease.
However, there are other less painful ways to conduct a test for peace of mind or to pin down your suspicions if a DH test comes back as negative.
An at-home celiac disease test kit from imaware™ is the best way to quickly and easily test for celiac disease. It only requires a small finger prick which can be conducted in your own home, and one sent back to the lab, results can be viewed online within 5 days.
Not only does this mean you don’t have to undergo a troublesome biopsy, but none of your health information can get lost in the post.
imaware™ uses the latest screening technologies alongside an additional 3 biomarkers to provide the most detailed and comprehensive results possible.
Results can be accessed at any time and can be easily sent onto a healthcare professional. Clear next-steps are provided with the results.
What is the treatment for celiac disease and dermatitis herpetiformis
 Although hard for people to accept, the only way to properly treat both of these conditions is to adopt a lifelong gluten-free diet. It can be difficult, although there are now plenty of gluten-free food options on the market andonline gluten-free meal plans.
Although hard for people to accept, the only way to properly treat both of these conditions is to adopt a lifelong gluten-free diet. It can be difficult, although there are now plenty of gluten-free food options on the market andonline gluten-free meal plans.
The skin’s response to the new diet is likely to be much slower than that of your internal system, so don’t be alarmed if your skin takes a while to clear up – it could take anywhere from 6 months to 2 years, unfortunately.
Your doctor can prove short-term relief from the itchiness in the form of dapsone, an antibacterial medication. The drug should kick in around 48 to 72 hours after the first dose.
What happens if celiac disease is left untreated?
Celiac disease can bring on a string of digestion problems if left untreated. As well as causing long-term stomach problems, the disorder can make it hard for the body to consume the nutrients it needs.
That’s because the immune system’s constant attack on the small intestine can cause severe damage to the villi, part of the small intestine’s lining which is used to absorb nutrients from food.
This is why so many people with the disorder struggle with anemia although seemingly consuming enough iron, as the body struggles to absorb it in the stomach.
In severe cases, untreated celiac disease can lead to diabetes, coronary artery disease, colon cancers, multiple sclerosis, nerve damage, and gastrointestinal infections, alongside other autoimmune diseases.
Article Submitted By Community Writer




