Legionnaire’s Disease is a flu-like condition that usually spreads through the mist. Mist is commonly found in public buildings with extensive water supply systems and air conditioning units. Those who smoke and people who are over 50 years of age are more vulnerable to these condition. Some people may also contract the disease and fail to notice due to the lack of symptoms.
As such, it helps to get the facts right about the Legionnaires’ disease. Read on to learn more.
It’s Not Transmissible
Legionnaire’s disease can’t be spread from one person to another. So, you shouldn’t keep away from friends or family members who have it. Instead, help them get the medical assistance and medication they need.
You can only get the disease through inhaling vapor, mist or steam that contains the bacteria. For example, breathing in water droplets from a hot tub that hasn’t been cleaned could lead to catching the disease.
It’s Preventable
Preventing this disease simply involves improving the conditions and maintenance of your plumbing systems and other public spots, such as spas and pools. This way, it’s possible to limit the growth of Legionella bacterium, which is responsible for the disease. Modern methods for dealing with the bacteria include superheating, monochloramine disinfection, and copper-silver ionization.
During an outbreak, proper measures, such as water source decontamination, can help prevent further spreading of Legionnaires’ disease.
First Known in 1976
Also known as the legion fever, Legionnaires’ disease was first detected in late July 1976 by American Legion members. This was after a convention of the American Legion in Philadelphia. The victims were affected by a type of pneumonia, which later came to be known as the Legionnaires’ Disease. Typically, the name is derived from the term “Legion.”
It was after the 1976 case that the public health officials were able to link the bacteria to other instances that occurred in 1968.
Legionella Bacterium causes it
In order to know more about Legionnaires’ disease, one needs to be aware of Legionnaires’ disease facts. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), 75 to 80 percent of the reported cases usually involved people aged 50 years and above. Also, 60 to 70 percent of the patients are generally male. The reason for this is because of their weak immune system. So, you’re likely to find it in nursing homes and hospitals where germs and bacteria tend to spread quickly.
Those who smoke, people with a severe lung disease, and those with weakened body immunity are likely to get sick when exposed to the Legionella bacterium, too.
It Can Lead to Complications
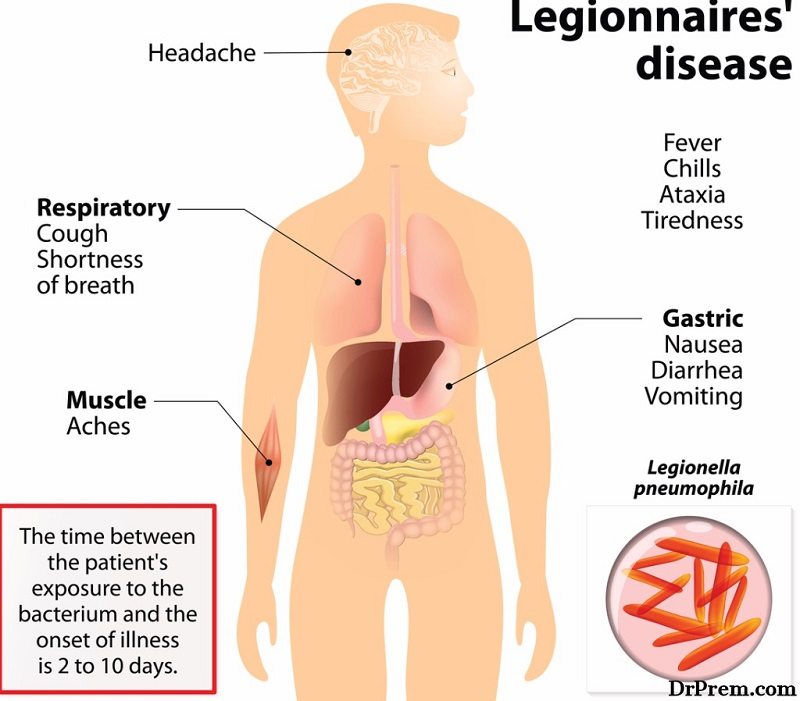
If left untreated or if it affects people who are already ill, it’s likely to lead to other health complications. For example, people with a severe lung problem can experience respiratory failure when they contract legionnaires’ disease. This is because the lungs may fail to supply adequate oxygen to the body or can’t remove carbon dioxide from the blood.
Other possible complications include septic shock and acute kidney failure. Legionnaires’ disease can be fatal when not treated promptly, so it helps to seek medical help as early as possible.
It’s Treatable
For typical cases, antibiotics are the recommended medications for treatment. Examples of antibiotic classes used in treatment include fluoroquinolones, macrolides, and the tetracyclines. Your doctor will prescribe the best possible treatment for you depending on your medication tolerance, clinical state, and the results of the diagnosis.
A mild form of Legionnaires’ disease known as Pontiac fever may require no treatment. It tends to clear away by itself over time.
Know the Facts!
Legionnaires’ disease is still a common condition, and its cases have been increasing by about four and a half times in the US since 2000, according to the CDC. Be sure to always seek early treatment if you think you have the condition.
Article Submitted by Community Writer.