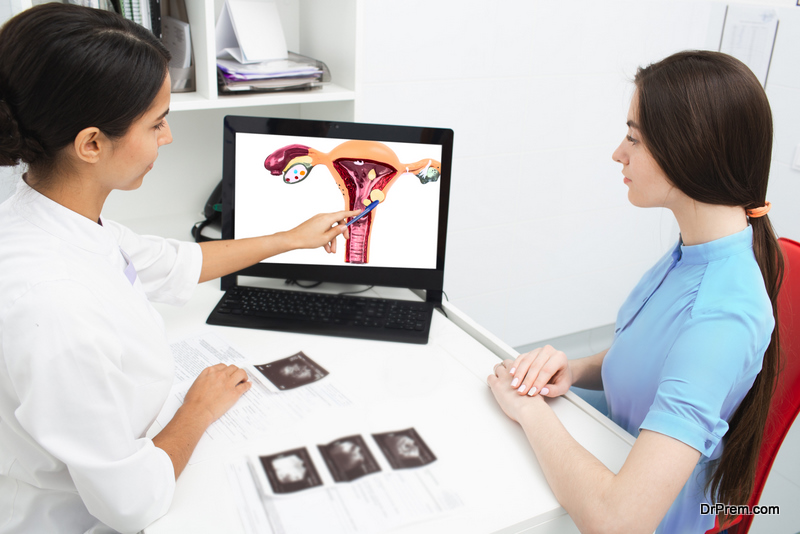
Fibroids are non-cancerous growths of the uterus. Fibroids grow and form mostly in women during their reproductive years, most often during their 30s and 40s.
Fibroids cause heavy periods (menorrhagia), causing 80 percent of cases. According to reports, incidence rates for fibroid diagnoses were highest for 45-49 years.
The best treatment for fibroids during pregnancy depends on the specific type and location of the uterine mass and its size and growth rate. Not all fibroids need to be treated during pregnancy, but some can cause pain or bleeding that warrants intervention.
The following article will explain the treatment options for fibroids during pregnancy and the relative risks and benefits of each procedure.
1. Myomectomy
Myomectomy is the surgical removal of fibroids. It may be open surgery, requiring a large incision to visualize the uterus, or an endoscopic surgery, which uses small incisions and a fiber-optic lighted tube with a camera attached (called a laparoscope) to visualize the uterus.
Myomectomy is one of the most effective treatments for fibroids during pregnancy, especially if the mother wishes to retain her fertility.
There are few reports of successful pregnancies after myomectomies; however, women who undergo successful myomectomies before pregnancy have no risk of miscarriage or premature birth.
2. Hysterectomy
Hysterectomy is the removal of the uterus, which in most cases necessitates removal of the cervix and ovaries as well. Although this procedure does not preserve fertility, it is common among women with children.
As with myomectomies, hysterectomies are not associated with an increased risk of miscarriage or preterm birth in pregnancy. However, this procedure requires a more significant recovery time and is more likely to cause complications.
3. Uterine Artery Embolization (UAE)
The procedure blocks the uterine arteries that supply blood to fibroids in a treatment known as uterine artery embolization (UAE). UAE is performed by injecting small particles into the uterine artery, such as tiny coils or beads. These particles cause the artery to become blocked, and the blood supply to the fibroid is cut off.
The procedure has been used in pregnant women since 2002, when its safety was first reported. It should be understood that this particular surgery is still considered experimental and has not been widely adopted as a first-line treatment for uterine fibroids.
4.Myolysis
Myolysis is the destruction of uterine muscle fibers through an enzyme directly into the uterus. The procedure does not require surgery but provides only short-term relief from fibroid symptoms.
5. Uterine artery embolization (UAE)
The procedure blocks the uterine arteries that supply blood to fibroids in a treatment known as uterine artery embolization (UAE). UAE is performed by injecting small particles into the uterine artery, such as tiny coils or beads. These particles cause the artery to become blocked, and the blood supply to the fibroid is cut off.
The procedure has been used in pregnant women since 2002, when its safety was first reported. It should be known that this procedure is still considered experimental and has not been widely adopted as a first-line treatment for uterine fibroids.
6. Fibroid Embolization (FEA)
Fibroid embolization (FEA or FEMR procedure) is a minimally invasive, catheter-based procedure that treats fibroids and the symptoms they cause by cutting off blood supply to the fibroid tumor. This process can shrink or eliminate uterine fibroids that cause pain, pressure, or bleeding.
7. Wedge Resection
Wedge resection (or myolysis is also known) is a uterine fibroid treatment. The physician uses surgical instruments to remove a section of the uterus’s muscle wall where the fibroid tumor is located. The remaining uterine muscle then “springs back” into place.
During pregnancy, the amount of time a woman spends lying on her back increases due to pressure from the fetus and rising hormone levels, known as body-surface forces. The excessive weight in the abdominal area compresses major blood vessels which supply blood to the pregnant uterus. The compression of these vessels can lead to a sharp fall in uterine blood flow.
A recent study has revealed that uterine artery embolization (selectively blocking the blood to non-vital organs), rather than a hysterectomy (removal of the uterus), is the better option for fibroids during pregnancy.
Symptoms of Fibroids in Pregnancy
Most women won’t experience any symptoms from fibroids growing in their uterus. But some may have:
- Increased menstrual bleeding, blood clots, or pain during periods
- Pressure in the pelvis, back, and stomach
- Trouble emptying the bladder or rectum (due to pressure on the bladder or large intestine)
- Urinary tract infections
If a woman has fertility problems, fibroids can also be the cause. Pressure from large fibroids may block the fallopian tubes or affect how an egg is released during ovulation. Fibroids that grow inside the uterine can interfere with the implantation of a fertilized egg in the uterus. In some cases, fibroids can lead to miscarriage.
Article Submitted By Community Writer