Yeast Infection: Diagnosis
Top Diagnosis
1. Culture test for vaginitis
This examination of the pelvic area is performed to diagnose the causes of vaginitis, a vaginal infection. Symptoms include itching, burning sensation, abnormal discharge with odor and pain during urination. The doctor uses a cotton swab to collect a sample of the vaginal discharge and views it under a microscope to look for candida organisms that cause vaginal yeast infections. This exam also assesses the health of your vagina, uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries so that any other abnormalities can be ruled out. This is an absolutely safe test as it does not involve any instrument contact or invasion. Just avoid any sexual intercourse before the test to facilitate easy working of the test.
2. Culture test for men
Since yeast infections are as common in men as in women, a culture test for men can also be performed. Looking for symptoms like rash on the penis or surrounding area, red or patchy sores near the foreskin, severe itching or burning sensation, whitish milk-like discharge near the head of the penis which is not semen. To diagnose the problem, the doctor usually takes a culture sample of the penile secretion and examines it under a microscope to confirm the presence of the Candida yeast. The sample is examined under a microscope via wet mount to distinguish the yeast flora. An absolutely non-invasive exam, it can be performed under a doctor’s guidance.
3. Oral culture
This test is done to determine the unusual growth of Candida albicans yeast in the mouth. Though its presence is quite common, the overgrowth can result in a strange infection. The symptoms range from white, creamy or yellow raised spots on the membranes in the mouth and tongue, burning or soreness, the throat, or at the corners of the lips. Diagnosis is usually done by looking at the lesions, brushing them to reveal a reddened, tender area that may bleed. A small sample is scrapped from the tongue and the tissue is examined under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis. This is a very simple test which involves no hospitalization, just a visit to an oral specialist is enough. The most common carriers of this infection are infants and children as they have low immunity levels, the elderly can also get affected by it easily.
4. Throat culture
The Candida yeast can even spread to your esophagus. In this test, a sterile cotton is used to swab at the throat’s back and the tissue sample cultured on a special medium to determine the kind of fungi. The condition can cause symptoms like pain or difficulty swallowing, feeling of food getting stuck mid way and in some cases, fever too. This too is a non-invasive test which can be performed by just one visit to the doctor.
5. KOH (potassium hydroxide) test
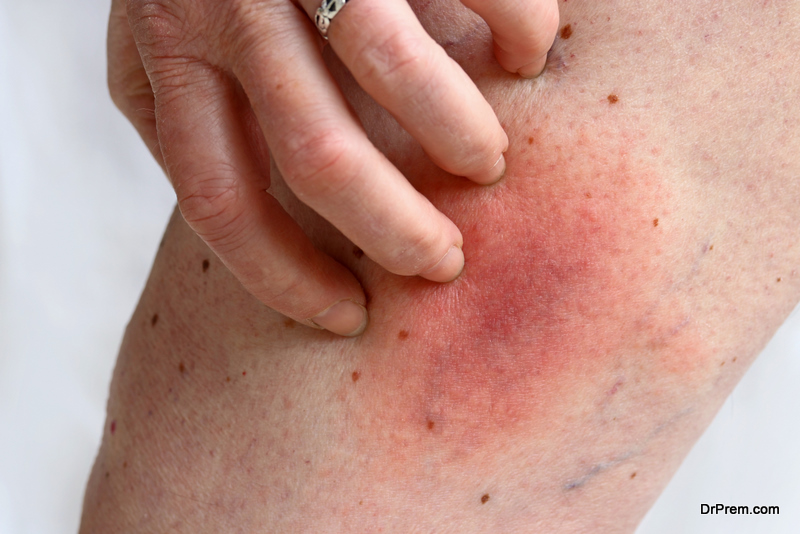
This preparation test is used to find the presence of yeast infection on skin. A sample of skin is collected by lightly scraping the infectious area. The skin sample is placed on a slide with KOH solution and heated gently. This solution slowly dissolves the skin cells but not the fungus cells which can be seen with a microscope. This test is conducted to determine symptoms such as patches of itchy skin, red, or scaly with blisters on the edges. Again a non-invasive and simple test, it calls for a regular doctor’s visit.
6. Calcofluor white stain
This very specific test involves placing the skin scrapings, hair or nail clippings on a slide to which calcoflour white stain, a chemical, has been added. The stain binds strongly to fungal elements and produces a fluorescent color when seen under a ultraviolet light. This transformation in turn allows better visualization on a microscope slide. Symptoms like itching, redness and rashes between the folds of the skin are usually diagnosed by this test. This test involves only an intense laboratory procedure, otherwise no hospitalization or patient observation is required.
7. Antibody blood test
A small blood sample is taken to detect yeast infection in a different way. It distinguishes the antibodies that exist in the Candida (yeast) fungus and measures its percentage. Antibodies like IgA, IgM and IgG are measured through this test. Their presence is crucial to determine whether your body has this infection. IgM antibodies indicate the present infection state in your body. IgG antibodies determine a previous infection and the IgA antibody reflects an infection that is on the outer surface of body’s mucosal linings. A simple blood test can be conducted at any diagnostic center.
8. Intestinal candida test
This is a stool test to check for good bacteria and yeast. Low or non-existent bacteria are a major cause of chronic yeast infections. If yeasts are detected in the test, it also makes way for getting a yeast susceptibility profile exam. This susceptibility test determines certain compounds and drugs useful in killing a specific kind of yeast. This specific yeast generally affects the gastrointestinal tract and can cause chest tightness, bloating or pain in the upper abdomen. A simple laboratory test can be ordered through a local doctor.
9. Fungal culture
A sample is collected and immunized into nutrient media and kept under incubation. This facilitates the growth of the fungus in a particular temperature. This test is generally performed to identify a specific kind of yeast. Skin, nail, hair, body fluids, sputum or blood are taken as samples. This is an all inclusive test for treating specific yeast related infections.