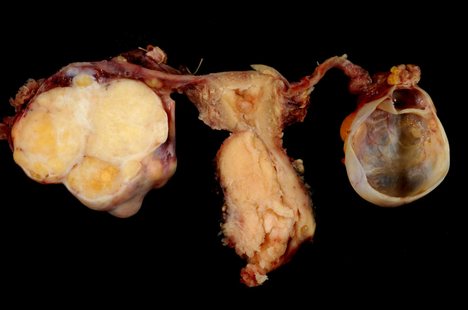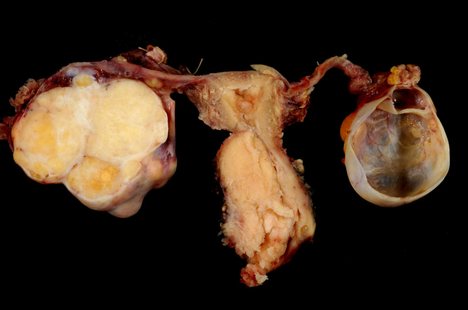
Cervical cancer is basically the cancer that occurs at the mouth of uterus. It is considered as the most common cancer among women. It is curable if detected at an early stage. Here are certain myths attached to it.
Cases of cervical cancer are found only in developing countries.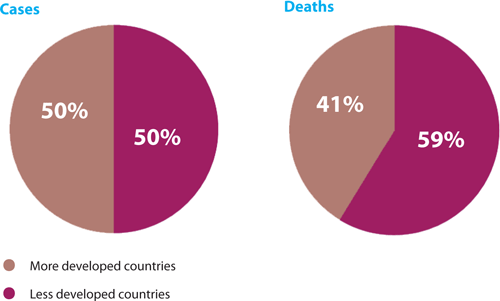 Cervical cancer is a disease that can plague any woman, irrespective of her color, ethnicity, or country. It is a fact that women in developing countries are at a greater risk of developing cervical cancer because of the lack of adequate screening programs. But, women in developed countries may also contract this disease. With new medications available, the risk is certainly lower in developed countries.You will develop cervical cancer if you are infected with HPV.
Cervical cancer is a disease that can plague any woman, irrespective of her color, ethnicity, or country. It is a fact that women in developing countries are at a greater risk of developing cervical cancer because of the lack of adequate screening programs. But, women in developed countries may also contract this disease. With new medications available, the risk is certainly lower in developed countries.You will develop cervical cancer if you are infected with HPV. Although, HPV is responsible for the maximum number of cases of cervical cancer, it does not imply that you will eventually develop cervical cancer if you have an HPV infection. In fact, this virus goes away on its own in most cases, and that too without any medical intervention. There are several other factors that contribute to the development of cervical cancer, aside from untreated high risk HPV infections. A regular cervical exam can decrease the risk significantly, as any changes can be detected by these tests long before they progress to cervical cancer.It is not possible to prevent cervical cancer.
Although, HPV is responsible for the maximum number of cases of cervical cancer, it does not imply that you will eventually develop cervical cancer if you have an HPV infection. In fact, this virus goes away on its own in most cases, and that too without any medical intervention. There are several other factors that contribute to the development of cervical cancer, aside from untreated high risk HPV infections. A regular cervical exam can decrease the risk significantly, as any changes can be detected by these tests long before they progress to cervical cancer.It is not possible to prevent cervical cancer.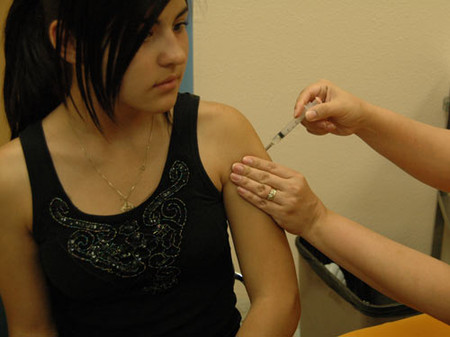 Cervical cancer falls into the category of one of the most preventable types of cancer. Regular pap smear testing is one of the effective ways of preventing cervical cancer. You must undergo these tests at regular intervals because pap smear test is a screening test and not a diagnostic test. Pap smear identifies women who are at higher risk of contracting this disease in comparison to others by identifying precancerous cervical changes. Gardasil, which is an HPV vaccine, is also found to be very effective at preventing cervical cancer.It is mostly promiscuous women who get cervical cancer.
Cervical cancer falls into the category of one of the most preventable types of cancer. Regular pap smear testing is one of the effective ways of preventing cervical cancer. You must undergo these tests at regular intervals because pap smear test is a screening test and not a diagnostic test. Pap smear identifies women who are at higher risk of contracting this disease in comparison to others by identifying precancerous cervical changes. Gardasil, which is an HPV vaccine, is also found to be very effective at preventing cervical cancer.It is mostly promiscuous women who get cervical cancer. One of the major risk factors for cervical cancer is having many sexual partners, but this is not the only risk factor and there are several others. Though the risk is low, women having only one partner can also develop cervical cancer.Contamination from cervical cancer causing virus can be prevented completely by using condoms.
One of the major risk factors for cervical cancer is having many sexual partners, but this is not the only risk factor and there are several others. Though the risk is low, women having only one partner can also develop cervical cancer.Contamination from cervical cancer causing virus can be prevented completely by using condoms.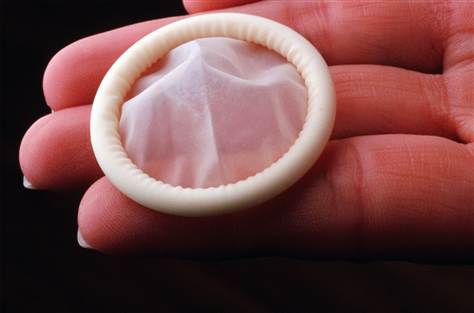 Condoms are definitely one of the effective barriers against HPV, but still they do not guarantee 100 percent protection. A condom covers only the penis, while the rest of the genitalia are left exposed. These may come in contact with the vagina during sexual intercourse. HPV can be transmitted through sexual as well as skin to skin contact with a person who is already infected, which means penetration is not essential for contracting the virus. However, this does not reduce the importance of condoms. Studies have shown that condoms have been found effective in 70 percent of the cases. It also protects you against several other STDs.The virus responsible for cervical cancer is not very common.
Condoms are definitely one of the effective barriers against HPV, but still they do not guarantee 100 percent protection. A condom covers only the penis, while the rest of the genitalia are left exposed. These may come in contact with the vagina during sexual intercourse. HPV can be transmitted through sexual as well as skin to skin contact with a person who is already infected, which means penetration is not essential for contracting the virus. However, this does not reduce the importance of condoms. Studies have shown that condoms have been found effective in 70 percent of the cases. It also protects you against several other STDs.The virus responsible for cervical cancer is not very common. One of the most popular myths regarding cervical cancer is that the virus responsible for contracting this disease (HPV) is not very common. However, the data collected from different sources contradict this view. HPV is extremely common. In fact, in the US itself over 20 million people are infected with HPV. It is also a fact that it is one of the most commonly sexually transmitted infections.All women need an annual pap smear to screen for cervical cancer.
One of the most popular myths regarding cervical cancer is that the virus responsible for contracting this disease (HPV) is not very common. However, the data collected from different sources contradict this view. HPV is extremely common. In fact, in the US itself over 20 million people are infected with HPV. It is also a fact that it is one of the most commonly sexually transmitted infections.All women need an annual pap smear to screen for cervical cancer. Earlier this view was considered to be true, but the updated cervical cancer guidelines state that all women need not have pap smear tests annually. There are several factors that determine the frequency of testing, some of which are previous test results, age, and the age when a women became sexually active.There is no need of pap smear for older women.
Earlier this view was considered to be true, but the updated cervical cancer guidelines state that all women need not have pap smear tests annually. There are several factors that determine the frequency of testing, some of which are previous test results, age, and the age when a women became sexually active.There is no need of pap smear for older women. This needs to be decided by your gynecologist, not by your age. Even older women need to have pap smear done. However, if the woman is above the age of 65 years and has not encountered an abnormal pap smear in the last 10 years, regular tests can be stopped. Talk to your doctor in case of any confusion.Women who have taken the vaccine don’t need pap smear tests.
This needs to be decided by your gynecologist, not by your age. Even older women need to have pap smear done. However, if the woman is above the age of 65 years and has not encountered an abnormal pap smear in the last 10 years, regular tests can be stopped. Talk to your doctor in case of any confusion.Women who have taken the vaccine don’t need pap smear tests.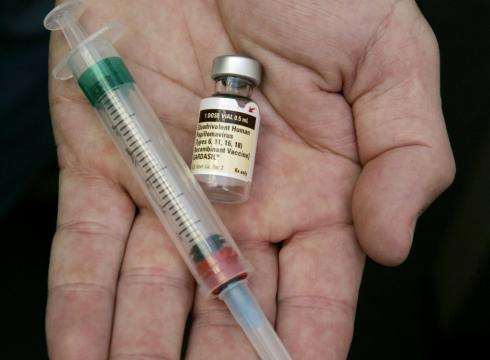 Getting vaccinated does not imply that you don’t need regular pap smear tests. Remember, Gardasil protects against two types of HPV which are responsible for the maximum number of cases. However, this does not mean that you are protected against the less common strains.
Getting vaccinated does not imply that you don’t need regular pap smear tests. Remember, Gardasil protects against two types of HPV which are responsible for the maximum number of cases. However, this does not mean that you are protected against the less common strains.