
It is needless to point out that the mother is the only source of supplying proper nutrition and food to a growing embryo. Dieting during pregnancy means restricting the correct values of nutrients required for the healthy growth and development of your baby which might lead to neurological disorders as well as other dietary malfunctioning in the baby.
Your doctor may prescribe you some prenatal vitamin tablets to provide the essential count of nutrients to the fetus, which would include a regular dosage of folate which assists in guarding against certain specific birth defects. Even then, you require a nutrient-rich diet which should include a variety of healthy food items comprising of all food groups namely, proteins, vitamins, minerals, iron, carbohydrates as well as fats. This balanced diet should include fortified whole grains, fruits, vegetables, proteins like meat, poultry, fish and eggs as well as dairy products, failing which the child would complain of unfavorable development and low growth statistics.
Nutritionists claim that a pregnant woman should intake about 2,500 calories from food every day which would suffice the growing needs of the mother as well as the baby and should put on approximately 25 to 35 pounds of weight to ensure a well developed baby at full term. However, you should concentrate more on the quality of your diet rather than the quantity during pregnancy so as to ensure a safe, healthy, secure and disease-free life for your little one.
Dieting could heighten risk of age related illnesses for the baby
Research reveals that women who maintain a low fat and unbalanced diet during pregnancy give birth to children who are more vulnerable to age-related diseases than those who have healthier diets and gain weight considerably. An experiment on rats proves the theory that if exposed to low protein diet during pregnancy, the young one develops high risks of type-2 diabetes and becomes more susceptible to effects of ageing in the early stages of life. Same is the case with humans where type-2 diabetes is said to determine the capacity of the body to produce and respond to insulin which is a hormone made by bete-cells in the pancreas.
A poor maternity diet leads to epigenetic alterations that tend to reduce the Hnf4a gene in the child. This gene in turn ascertains and governs the number of insulin producing cells that would grow in the pancreas which would further affect the organ’s ability to respond to the presence of high blood sugar levels in the blood. If the child develops type-2 diabetes at a young age, he is exposed to greater risks of suffering from cardiovascular diseases in later life as type-2 diabetes is a significant contributing factor to fatal heart diseases as well as cancer. So, do not risk your child’s well being at the cost of staying slim and trim, at least during the nine months when you are carrying a new life in your womb.
Dieting during pregnancy increases risk of premature birth
Dieting at the time of pregnancy can result in causing serious health hazards which can prove to be threatening for your little one. If you do not put on the ideal amount of weight required for the optimum growth and development of your child you would be putting yourself as well as your child’s life to a great deal of risk. Losing weight during this period can lead to a pre-mature delivery, thereby exposing the new life to unfavorable and unforeseen health issues right from birth.
These problems can range from breathing difficulties to even death of your child. By God’s grace, even if he manages to survive, he would be more likely to have grasping and learning difficulties as well as behavioral abnormalities, retardation, weakness in the lungs, cerebral palsy, vision or hearing impairments. Gynecologists state that a baby is considered to be born at term if he manages to remain inside his mother’s body for at least 37 weeks, going up to 42 weeks. Anything less than the minimum duration is judged as a pre-term baby born with low immunity and high risks of diseases.
Your baby could be born suffering from malnutrition
Your weight gain during pregnancy is the indication that your unborn child is being nourished well which is so very important for her physical as well as mental growth. If you undertake to diet during this time, your child would remain bereft of the proper amount of calories essentially needed to provide overall nourishment for her all round development. This could result in delivering a baby with low birth weight and malnourishment. The baby would also be judged as being small as per her gestational age if the mother does not gain at least 20 pounds of weight during the total span of her pregnancy, thereby causing serious health issues for the newborn.
Dieting could affect your breast feeding ability
It is a proven fact that a certain percentage of weight gain during pregnancy is kept aside and stored for calorie utilization for breast feeding the baby. This is why most women lose weight at a very quick pace while indulging in breast feeding once the baby is born. Not gaining enough ideal weight during pregnancy can result in inadequacy and inability to feed your baby, thereby having negative effects on the growth of the young one. If this is the case with you, consult your obstetrician for advice.
Undernourishment of fetus could lead to improper genetic composition
It is a well established truth that environmental factors impact genes interaction throughout the lifespan of an individual, thereby influencing genetic expression and tissue functioning. This also has an effect on the risks of diseases attached to these genes. Dieting at crucial developmental stages, when the child is in his mother’s womb, works as a guiding force which influences these environmental factors. The production of the quantity of genes is regulated by the DNA content, which in turn is modified by epigenetics which underline these effects.
A good maternity diet can mark those genes which enables the child to remember events taking place in very early life, thereby enhancing memory and concentration. A mother’s dietary intake alters and has a considerable influence in controlling certain genes within her unborn baby. These minor alterations within the cells at the very early stages of development can have major influence on the health of the yet-to-be-born child, especially in his later stages of life. Dieting during pregnancy can never promote proper composition of these genes, thereby leading to reduced resistance, low memory and low susceptibility to fight major fatal diseases later on in life.
Dieting while pregnant increases risk of obesity in your child
The mother’s food intake during pregnancy can lead to alteration of the DNA levels of her little one and expose the child to increased risks of obesity. Low levels of carbohydrate intake can change bits of DNA. Statistics prove that children born with these changes are overweight as compared to those without them. This happens because a growing baby can predict the surrounding it would be born in by taking cues from the mother and thus adjusts its DNA accordingly. Dieting during pregnancy can even raise chances of pre-ecclampsia or gestational hypertension condition in the baby. So, it is necessary for a pregnant woman to gain weight, and give up practices of dieting for the well-being and betterment for her growing child.
Your dieting can impact brain development of your child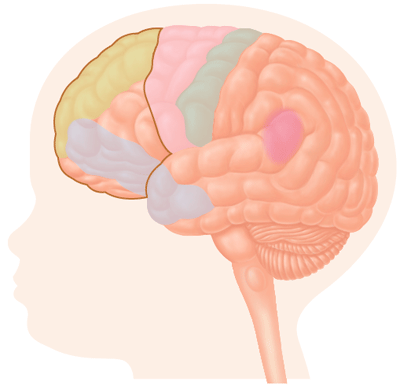
Nutritionists all across the world believe that a pregnant woman should eat an additional 300 calories every day to make up for extra energy spent. It is a known fact that the most vital food for brain efficiency, growth and sharpness is glucose. There should be a continuous and uninterrupted supply of glucose to the brain of the fetus for it to absorb and grow fully. Any carbohydrate-spare diet regime followed during pregnancy, in a attempt to cut down on excess weight gain, can deprive the fetus’s brain of glucose content, thereby leading to the occurrence of Ketosis which is a disease acquired when the fetal brain is deprived of glucose and other essential nutrients, hence jeopardizing its progress and proper development.
Dieting during pregnancy can lead to
A low diet intake due to fasting for long hours, dieting to shed excess weight and switching to a calorie-restricted diet or adapting to any other form of eating disorders at the time of pregnancy can lead to the baby suffering from higher risks of developing neural tube defects in the initial stages itself i.e., by the first trimester of pregnancy. These diseases include spina bifida and anencephaly which restrict fetal growth and can even claim his life.
Undernourished women give birth to babies with low birth weight
It is an obvious fact that if a woman does not gain the appropriate amount of weight at the time of pregnancy her baby too would be born with a low birth weight. A calorie-restricted diet is not fully equipped with minerals and vitamins. Increased quantities of calcium, iron, zinc and magnesium are mandatory and most essential to ensure proper and full development of the baby’s bones, teeth, blood and other vital organs as well. Not meeting the daily requirement values of these essential nutrients during pregnancy would put a question mark on the safety, growth, ideal birth weight and proper fetal development and lead to unnecessary complications for the mother as well as the child.


